CSS
Background image
-
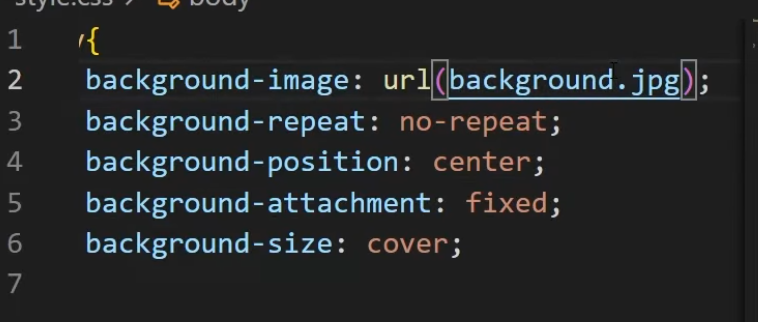 .
.
Selectors
Selecting
-
By Element
h1 {
}
-
By Class, with
..
.secondary {
}
-
By ID, with
#.
#main-text {
}
Attribute selector (
[]
)
-
Removes the 'Change sorting' functionality and icon by selecting the attribute.
[aria-label="Change Ordering"] {
display:none;
}
-
Using
aria-label=gives a string match. Usingaria-label*=gives a substring match.
Chaining
-
Using
,.
h1, h2 {
}
Inside of
-
Using
h1 h2 {
}
-
"
h2tags that have ah1as their parent".
One Level Deep (Children)
-
Using
>.
.hero > h2 {
}
-
The
>(child combinator) is used to select only the immediate children of thebodyelement that also have the classes specified. -
In the example above, select children of the class
.herothat have anh2element.
Everything Selector (
*
)
-
Selects everything in the entire web page.
* {
font-family: Arial;
}
Styling and Attributes
Attributes
-
It's what goes inside a style.
-
color,padding, etc.
Specificity
-
More specific selectors get priority.
-
The order is:
ID > Class > Element.
Important
!important
Closest vs Contains
-
Use
closestwhen you want to find the closest ancestor matching a selector. -
Use
containswhen you want to check if one element is a descendant of another. -
In your click event handling, you might use
closestto determine if the clicked element or any of its ancestors has a specific class. This is helpful when you want to capture clicks on or within a specific container. On the other hand,containsis used to directly check if one element contains another.
Box Model
-
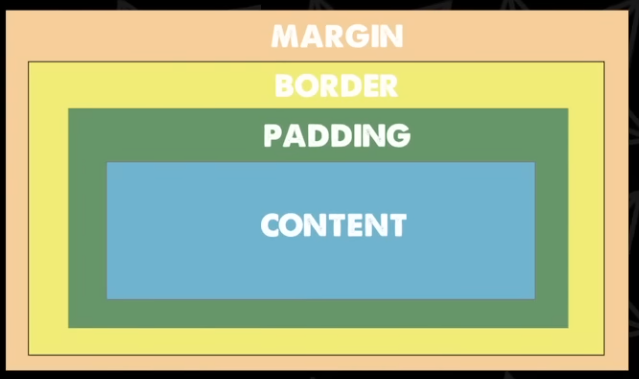 .
.
Content
-
width,height-
Can be set as
%of the parent container.
-
-
text-align-
To position things inside the content.
-
-
background-color-
Is applied to content and padding.
-
Padding
.hero {
/* All sides */
padding: 10px;
/* top and bottom, left and right */
padding: 10px 20px;
/* top, right, bottom, left (it's clockwise, if it helps) */
padding: 10px 20px 30px 40px;
}
Border
.hero {
/* size type color */
border: 1px solid black;
}
Margin
.hero {
/* All sides */
margin: 10px;
/* top and bottom, left and right */
margin: 10px 20px;
/* top, right, bottom, left (it's clockwise, if it helps) */
margin: 10px 20px 30px 40px;
}
Display
-
.
Units
Pixels
-
Absolute measurement.
REM
-
Relative to the base font size.
-
Changing the font size will change the spacing of everything.
Position
relative
-
The element stays in the normal flow .
-
You can use
top,left,right,bottomto offset it visually , but the space it occupies in the document does not change . -
Other elements still behave as if it’s in the original position .
absolute
-
The element is removed from the normal flow .
-
It is positioned relative to the closest ancestor with
position: relative|absolute|fixed. -
Other elements behave as if it doesn’t exist , so it doesn’t affect layout height or width.
Pseudo-Classes
-
:hover -
:first-child -
:nth-child(2)
Pseudo-Elements
Marker
-
Reason to use
::beforeinstead:-
::markerhas limited styling . You can’t useposition,transform, orflexboxon it. -
::markerinherits color and size but cannot be freely moved. -
::beforeis a normal pseudo-element , so it supports full layout control: absolute positioning, transforms, scaling, etc.
-
-
Use
::markerfor simple, semantic bullets when default positioning is fine. -
Use
::beforewhen you need custom placement, animation, or different symbols per nesting level.
Before
-
.
After
-
.
Media Queries
-
Allows styling for mobile or different screen sizes.
-
Triggered by "breakpoints".
/* else */
body {
background-color: blue;
}
/* if this condition passes (if the width is less than 600px), use this style */
@media screen and (max-width: 600px) {
body {
background-color: olive;
}
}
Operations
Ternary Operations (
?
and
:
)
-
The
?and:are part of the ternary conditional operator, which is a shorthand way of writing anif-elsestatement in a single line. The expression before the?is evaluated, and if it's true, the value before the:is used; otherwise, the value after the:is used.
Pre-processors
Sass
-
CSS can do everything this can.
-
Entire different language to learn.
-
.scssfile. -
Never.
CSS-IN-JS
JSS
-
.
Styled Components
-
.
Emotion
-
.
Styletron
-
.
Utility Classes
-
Big commitment.
-
No components.
Tailwind
-
.
Frameworks
Bootstrap
-
.
Bulma
-
.
Debugging
-
Freezing the screen to inspect something with DevTools:
-
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17931571/freeze-screen-in-chrome-debugger-devtools-panel-for-popover-inspection.
-
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/28963272/how-can-i-inspect-html-element-that-disappears-from-dom-on-lost-focus.
-