Security
Inspect Site
Web Scanners
VirusTotal
-
-
(2025-11-02)
-
My github pages site passed.
-
-
Quick multi-engine check.
-
Open VirusTotal, paste the URL in the URL field, hit search.
-
If any engines or community reports mark it malicious, do not open.
-
Why use it: it checks the URL against many antivirus and blacklist engines at once.
urlscan.io
-
-
(2025-11-02)
-
My github pages site passed.
-
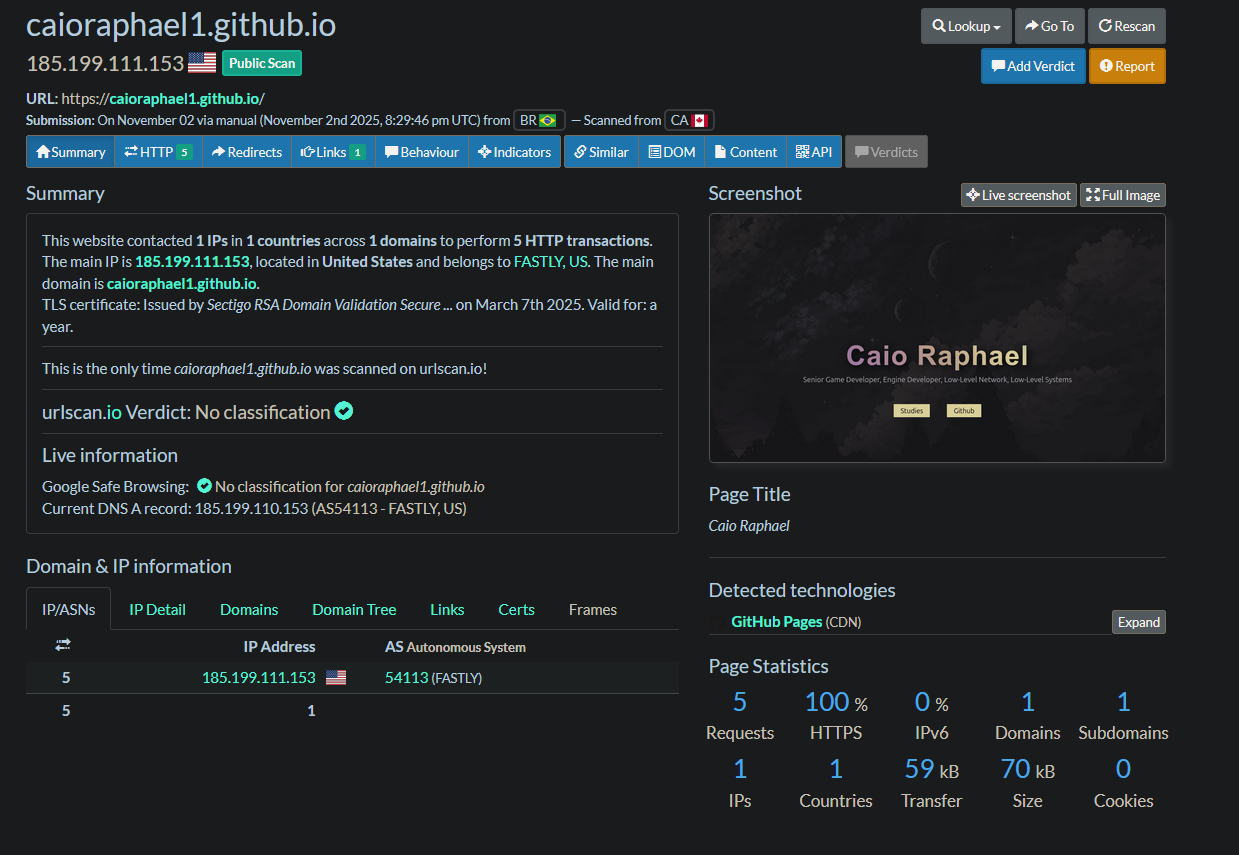 .
.
-
-
live page snapshot and resource list.
-
Paste the URL and run a scan (use Unlisted/Private if the link is private).
-
Look at the screenshot, the list of external hosts, and the resource requests. If you see strange redirects or many unknown hosts, avoid the page.
-
Note: public scans are visible to others. Use private mode for sensitive URLs.
Google Safe Browsing / Transparency Report
-
-
(2025-11-02)
-
My github pages site passed, I think. It showed "No available data" as the result.
-
-
Enter the URL into Google’s Safe Browsing lookup. It reports phishing/malware listings used by Chrome and other products. If flagged, do not open.
HTTP Headers
-
These tools let you probe the network behavior of a site safely at the protocol level, before any code or file is executed locally.
-
curl -I https://example.com-
Sends a
HEADrequest (fetches only headers). -
Check
Location,Set-Cookie,Content-Type,Content-Length,Server. -
Expect
Strict-Transport-Security,Content-Security-Policy,X-Content-Type-Options,Referrer-Policy,X-Frame-Options. Absence is a risk signal. -
If you see:
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently Location: http://malicious.example.com-
you know to avoid visiting it the site.
-
-s-
Silent
-
-
-L-
follow redirects.
-
-
-k-
ignore certificate verification (not advised except for testing).
-
-
-J-
use
Content-Dispositionheader filename (when present).
-
-
-v-
verbose mode; shows SSL/TLS handshake details.
-
-
-o-
write output to file.
-
-
-O-
save to remote filename
-
-
Note :
-
Works on CMD, not on PowerShell.
-
-
-
wget --spider https://example.com-
Makes a lightweight request to test if a URL exists or redirects.
-
It prints connection info, HTTP status, and redirection chain.
-
It doesn’t download or store the page body.
-
--server-response-
shows headers.
-
-
--max-redirect=0-
stops following redirects to detect them manually.
-
-
--no-check-certificate-
skip TLS verification (for testing only).
-
-
No JavaScript
-
Download raw HTML without executing resources.
-
curl -sL https://example.com -o page.html -
Inspect with
less,sed, orgrepfor<script src=...>,eval(,new Function, large base64 blobs.
-
-
View text-only render.
-
Useful to spot social engineering copy, visible links, and inline URLs.
-
lynx -dump https://example.com-
Lynx fetches the page like a normal browser but does not run JavaScript. It follows HTTP(S) and shows forms as text.
-
Safer than a full browser because no client-side script execution. Still makes network requests.
-
Prints to stdout.
-
-
or
-
w3m -dump https://example.com-
Same category as Lynx, but formatting differs.
-
Renders HTML to plain text and prints it.
-
-
Helps spot social-engineering text and visible links.
-
Network, DNS, Ownership
-
DNS records and delegation.
-
dig +short example.com A AAAA CNAME -
dig +trace example.com -
Look for unexpected CNAMEs, CDN hosts, or external domains.
-
-
WHOIS and registrar.
-
whois example.com -
Check creation date, registrar, contact, privacy proxy.
-
-
Reverse IP / hosting.
-
host example.comordig +short @8.8.8.8 example.comthenwhois <ip> -
See if many unrelated sites share the IP.
-
Capture packets
-
tcpdump -i any host example.com-
Capture packets to/from
example.comon all interfaces. -
You see raw packet-level traffic. TCP SYN/ACK, HTTP requests and responses if not encrypted, TLS handshakes, DNS queries.
-
Typical use: run while loading a page in an isolated browser to record all outbound connections.
-
Encrypted payloads remain encrypted. Captures can contain sensitive info. Store captures securely. Requires root/administrator privileges.
-
-w capture.pcap-
save
-
-
-nn-
numeric addresses/ports
-
-
-s 0-
capture full packets.
-
-
-
nmap -sV -p- example.com-
Port/service scan.
-
Probe all TCP ports (
-p-) and attempt to identify service versions (-sV). -
What you see: open ports, service names, version fingerprints, possible OS hints.
-
Useful to: find exposed management interfaces or unexpected services.
-
Risk note: scanning may be logged or blocked. Some networks treat it as hostile. Obtain permission.
-
TLS Certificate
-
Inspect cert chain and ciphers.
openssl s_client -connect example.com:443 -servername example.com -showcertsCheck validity dates, issuer, SANs, weak ciphers. -
Quick cipher list.
nmap --script ssl-enum-ciphers -p 443 example.com