Assembly - ASM
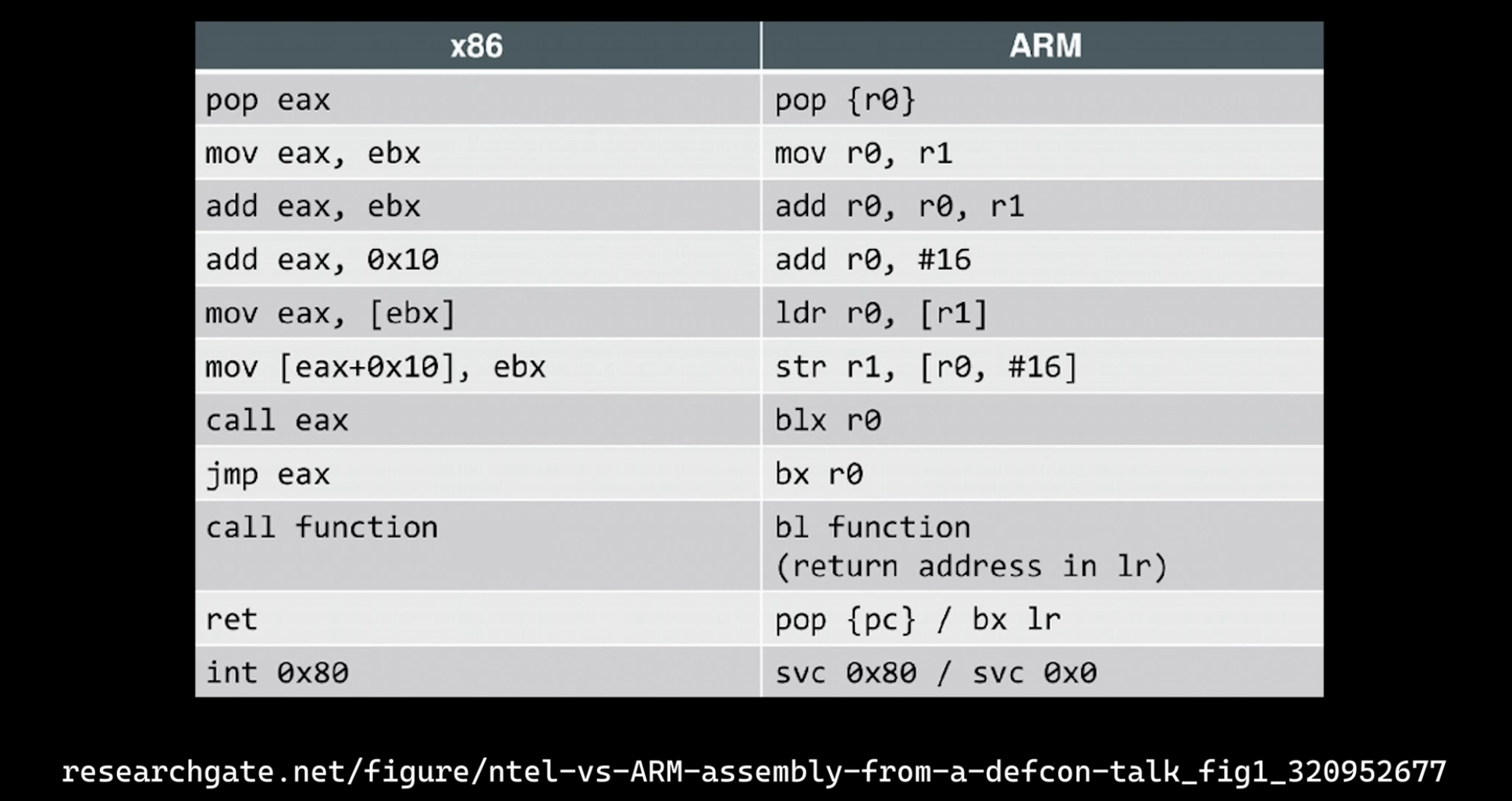
-
Not portable.
Where I stopped
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kKtWsuuJEDs&list=PLn_It163He32Ujm-l_czgEBhbJjOUgFhg
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wLXIWKUWpSs&list=PLmxT2pVYo5LB5EzTPZGfFN0c2GDiSXgQe
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yBO-EJoVDo0&list=PL2EF13wm-hWCoj6tUBGUmrkJmH1972dBB
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gfmRrPjnEw4
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vcSijrRsrY0
-
https://www.youtube.com/@LearnWithMxy/videos
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u_-oQx_4jvo
Notes
-
Think of the
[ ]as the dereference operator in C.
Reverse Engineering
Operations
Move Operations
-
mov:-
Copies data from source to destination. Does not modify flags.
-
Ex :
mov eax, 5(copies 5 into eax).
-
-
movzx:-
Move with zero extension (for unsigned values).
-
Ex :
movzx eax, bl(copies bl into eax, zeroing upper bits).
-
-
movsx:-
Move with sign extension (for signed values).
-
Ex :
movsx eax, bl(copies bl into eax, sign-extending).
-
-
xchg:-
Exchanges values between two operands.
-
Ex :
xchg eax, ebx(swaps eax and ebx).
-
-
lea:-
Load Effective Address (computes address without dereferencing).
-
Usually used to obtain a pointer to a memory region.
-
Ex :
lea eax, [ebx+4](stores ebx+4 in eax).
-
Arithmetic Instructions
-
Perform mathematical operations.
-
add:-
Adds two operands.
-
Ex :
add eax, ebx(eax = eax + ebx).
-
-
sub:-
Subtracts the second operand from the first.
-
Ex :
sub eax, 5(eax = eax - 5).
-
-
inc:-
Increments by 1.
-
Ex :
inc eax(eax++).
-
-
dec:-
Decrements by 1.
-
Ex :
dec eax(eax--).
-
-
mul:-
Unsigned multiply (stores result in eax/edx:eax).
-
Ex :
mul ebx(eax * ebx, result in edx:eax).
-
-
imul:-
Signed multiply.
-
Ex :
imul eax, ebx(eax = eax * ebx).
-
-
div:-
Unsigned division (divides edx:eax by operand).
-
Ex :
div ebx(edx:eax / ebx, quotient in eax).
-
-
idiv:-
Signed division.
-
Ex :
idiv ebx(same as div but signed).
-
-
neg:-
Negates a value (two's complement).
-
Ex :
neg eax(eax = -eax).
-
Bitwise and Logical Instructions
-
Perform bit-level operations.
-
and:-
Bitwise AND.
-
Ex :
and eax, ebx(eax = eax & ebx).
-
-
or:-
Bitwise OR.
-
Ex :
or eax, ebx(eax = eax | ebx).
-
-
xor:-
Bitwise XOR.
-
Ex :
xor eax, eax(sets eax to 0).
-
-
not:-
Bitwise NOT (inverts bits).
-
Ex :
not eax(eax = ~eax).
-
-
shl:-
Shift left (logical shift).
-
Ex :
shl eax, 2(eax << 2).
-
-
shr:-
Shift right (logical shift).
-
Ex :
shr eax, 2(eax >> 2).
-
-
sal:-
Arithmetic shift left (same as shl).
-
Ex :
sal eax, 2.
-
-
sar:-
Arithmetic shift right (preserves sign).
-
Ex :
sar eax, 2.
-
Control Flow Instructions
-
Change the execution flow (branches, loops, calls).
-
jmp:-
Unconditional jump.
-
Ex :
jmp label(jumps to label).
-
-
je/jz:-
Jump if equal/zero (ZF=1).
-
Ex :
je label(jumps if ZF=1).
-
-
jne/jnz:-
Jump if not equal/zero (ZF=0).
-
Ex :
jne label(jumps if ZF=0).
-
-
jg/jnle:-
Jump if greater (signed).
-
Ex :
jg label(jumps if SF=OF and ZF=0).
-
-
jl/jnge:-
Jump if less (signed).
-
Ex :
jl label(jumps if SF≠OF).
-
-
ja/jnbe:-
Jump if above (unsigned).
-
Ex :
ja label(jumps if CF=0 and ZF=0).
-
-
jb/jnae:-
Jump if below (unsigned).
-
Ex :
jb label(jumps if CF=1).
-
-
call:-
Calls a function (pushes return address).
-
Ex :
call func(calls func).
-
-
ret:-
Returns from a function (pops return address).
-
Ex :
ret.
-
-
loop:-
Decrements ecx and jumps if not zero.
-
Ex :
loop label.
-
Stack Operations
-
Manipulate the stack.
-
push:-
Pushes a value onto the stack.
-
Ex :
push eax(decrements esp, stores eax).
-
-
pop:-
Pops a value from the stack.
-
Ex :
pop eax(loads eax, increments esp).
-
-
pusha/pushad:-
Pushes all general-purpose registers.
-
Ex :
pusha(x86).
-
-
popa/popad:-
Pops all general-purpose registers.
-
Ex :
popa(x86).
-
Comparison and Flag Instructions
-
Modify or check CPU flags.
-
cmp:-
Compares two operands (subtracts without storing).
-
Ex :
cmp eax, ebx(sets flags based on eax - ebx).
-
-
test:-
Bitwise AND (without storing result).
-
Ex :
test eax, eax(sets ZF if eax=0).
-
-
stc:-
Sets Carry Flag (CF=1).
-
Ex :
stc.
-
-
clc:-
Clears Carry Flag (CF=0).
-
Ex :
clc.
-
System and Miscellaneous Instructions
-
Interact with the CPU/system.
-
int:-
Generates a software interrupt.
-
Ex :
int 0x80(Linux syscall).
-
-
nop:-
No operation (does nothing).
-
Ex :
nop.
-
-
hlt:-
Halts the CPU.
-
Ex :
hlt.
-
-
syscall:-
Fast system call (x86-64).
-
Ex :
syscall(Linux).
-
-
iret:-
Returns from an interrupt.
-
Ex :
iret.
-
String Operations
-
Work with strings (uses esi, edi).
-
movsb:-
Moves byte from
[esi]to[edi]. -
Ex :
rep movsb(copies a string).
-
-
cmpsb:-
Compares bytes at
[esi]and[edi]. -
Ex :
rep cmpsb.
-
-
stosb:-
Stores al into
[edi]. -
Ex :
rep stosb(fills memory).
-
-
lodsb:-
Loads byte from
[esi]into al. -
Ex :
lodsb.
-
Floating-Point Instructions
-
Floating-point math (x87/SSE).
-
fadd:-
Floating-point add.
-
Ex :
fadd st0, st1(st0 += st1).
-
-
fmul:-
Floating-point multiply.
-
Ex :
fmul st0, st1.
-
-
fld:-
Loads float onto FPU stack.
-
Ex :
fld dword [x].
-
-
fstp:-
Stores float and pops stack.
-
Ex :
fstp dword [y].
-