App signing
Keystore and Keys
-
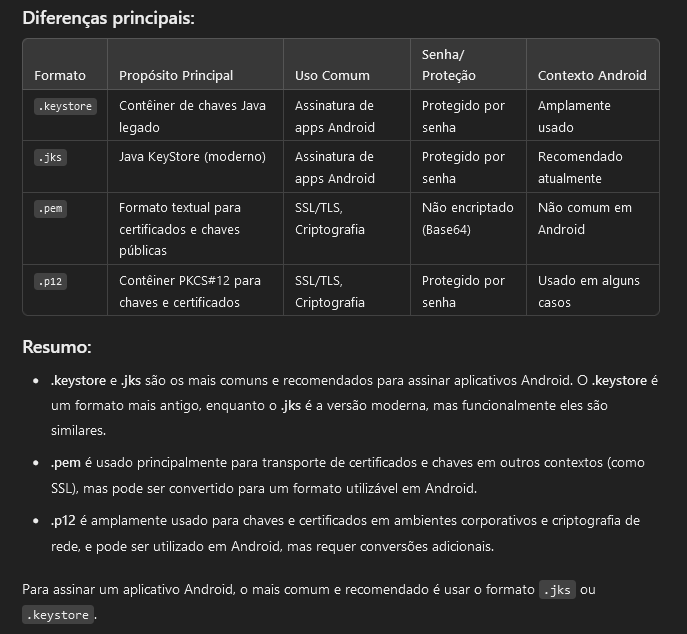
Keystore :
-
The secure place (or service) where keys are stored and managed, protecting them against theft or misuse.
-
-
Key :
-
The cryptographic key itself, which can be used for operations like encryption and signing.
-
Types of Keys
-
Key
-
Upload Key
-
The upload key is used only to sign the APK before uploading it to Google Play. After upload, Google replaces that signature with the official signature managed by Google's signing service using the real signing key .
-
Therefore, the upload key is an intermediate key to ensure the security of the upload process and maintain the integrity of the app.
-
If the upload key is compromised or lost, the developer can request a new upload key from Google without losing access to the app or the ability to update it.
-
-
Signing Key
-
Usually generated by Google.
-
The signing key is the cryptographic key used to sign the final APK (Android application package) that will be installed on users' devices.
-
The digital signature with the signing key ensures that the app code has not been modified since it was signed. It confirms the developer's identity, as each signing key is unique.
-
This key is essential and must be kept secure, since any update to the app will also need to be signed with the same key.
-
If the signing key is lost, you will no longer be able to update the app published on the Play Store.
-
-
-
Debug Key
-
The debug key is automatically generated by Android Studio (or the build tools) when you build an app in debug mode.
-
It is stored in a default keystore location, usually:
-
For Windows:
C:\Users\<username>\.android\debug.keystore -
For macOS/Linux:
/home/<username>/.android/debug.keystore
-
-
The debug key has a fixed alias (
androiddebugkey) and a default password (androidfor both the keystore and the key).-
This always happens.
-
-
Its validity is short (usually 365 days).
-
It is used only during development and testing and cannot be used to distribute apps on the Google Play Store.
-
An APK signed with the debug key cannot be published on the Play Store.
-
"Can I manually generate a debug key?"
-
If you want to manually generate a debug key, you can create a key with the same characteristics as a debug key, such as alias, password and validity, using the
keytoolcommand. However, it is important to remember that even if you generate a key with those characteristics, it will not be considered an "official debug key" used automatically by Android Studio to build debug-mode apps. -
It is possible to identify whether a key is an official debug key or a manually generated key with the same characteristics. This can be done by analyzing some information of the key, such as alias, location, passwords and issuer.
-
Even if the key is not an official debug key, it will not be accepted by the Play Store due to its set of characteristics similar to an official Debug Key.
-
-
Generating a Keystore
-
keytool -v -genkey -keystore mygame.jks -alias mygame -keyalg RSA -validity 10000 -
This generates a Key that can be either an Upload Key or a Signing Key .
-
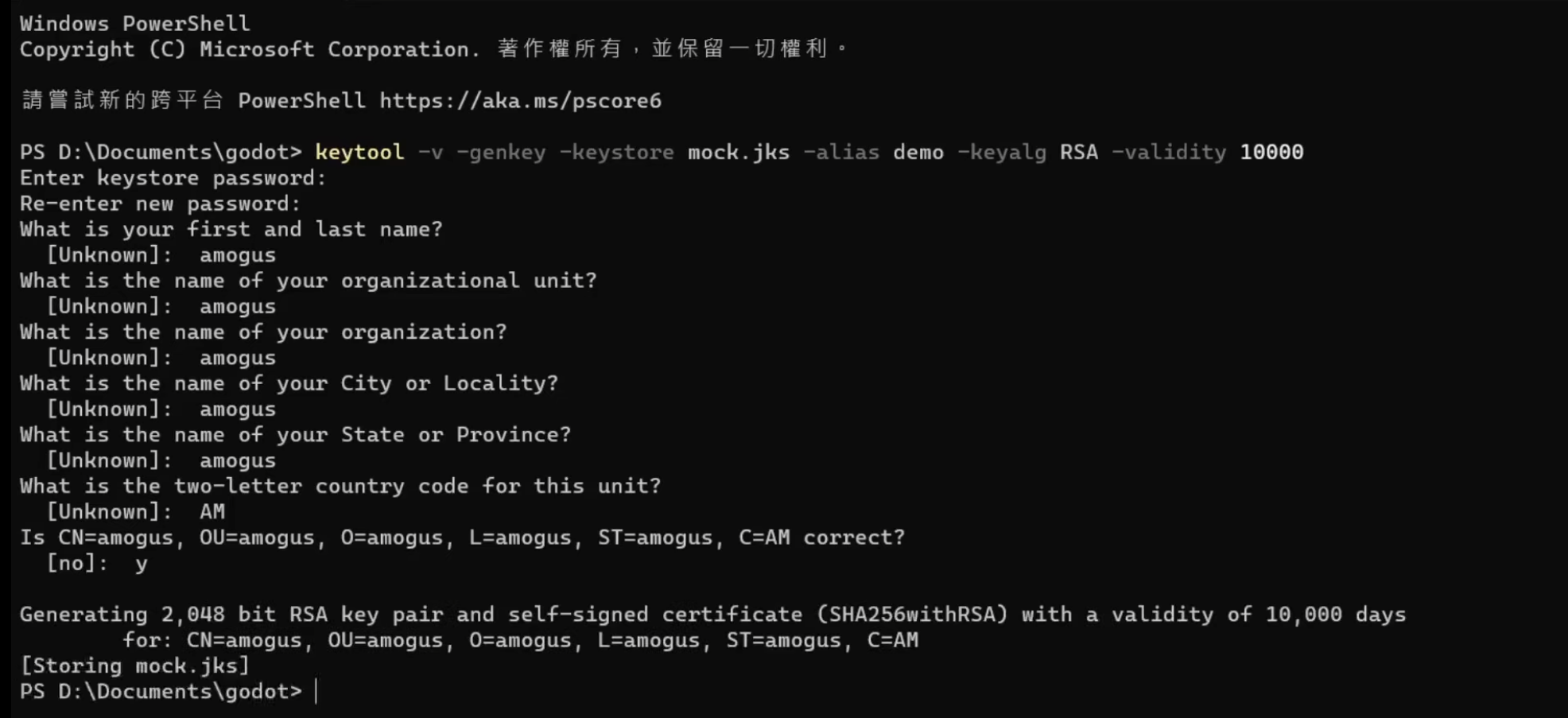 - This is a screenshot from a video, btw.
- This is a screenshot from a video, btw.
Signing extensions
-
 .
.
.apk.idsig
-
The
.apk.idsigfile contains digital signing information required to validate and verify the APK's integrity on the Android system. -
It is generated automatically by Godot and is part of the APK export and signing process.
-
You do not need to manipulate it directly. The Android system uses it internally when installing the APK to ensure that the signature is valid.
-
The
.apk.idsigfile is not generated when exporting an.aab(Android App Bundle). The.idsigis specifically associated with the APK format, which is the directly installable package on Android devices. The.aab, on the other hand, follows a different signing and packaging process. -
Renaming the file and removing the
.apkprefix from the.apk.idsigwould likely cause problems** during the APK signature verification on the Android system. This happens because the installation and verification process for APKs in Android depends on a specific file structure and naming conventions that tie the digital signature to its corresponding APK.
Fingerprints
-
The certificate fingerprint is a short and unique representation of a certificate that is often requested by API providers alongside the package name to register an app to use their service. The MD5, SHA-1 and SHA-256 fingerprints of the upload and app signing certificates can be found on the app signing page of the Play Console. Other fingerprints can also be computed by downloading the original certificate (
.der) from the same page.
Considerations
-
App upgrade:
-
When the system is installing an update to an app, it compares the certificate(s) in the new version with those in the existing version. The system allows the update if the certificates match. If you sign the new version with a different certificate, you must assign a different package name to the app—in this case, the user installs the new version as a completely new app.
-
-
Code/data sharing through permissions:
-
Android provides signature-based permissions enforcement, so that an app can expose functionality to another app that is signed with a specified certificate. By signing multiple APKs with the same certificate and using signature-based permissions checks, your apps can share code and data in a secure manner.
-
I have no idea about this.
-
Google Play Store
Developer Account
-
A one-time fee of 25 USD is charged.
-
(2024-10-18) I paid the 25 USD fee (?? BRL) and submitted my ID and proof of address for verification.
Fees
-
If your app is paid or if you have in-app purchases, Google takes a percentage of each sale.
-
The standard commission is:
-
15% for the first US$1 million in annual revenue per developer.
-
30% for annual revenue above US$1 million.
-
-
This applies to paid apps and to purchases made within free apps (such as subscriptions or virtual items).
.aab vs .apk
-
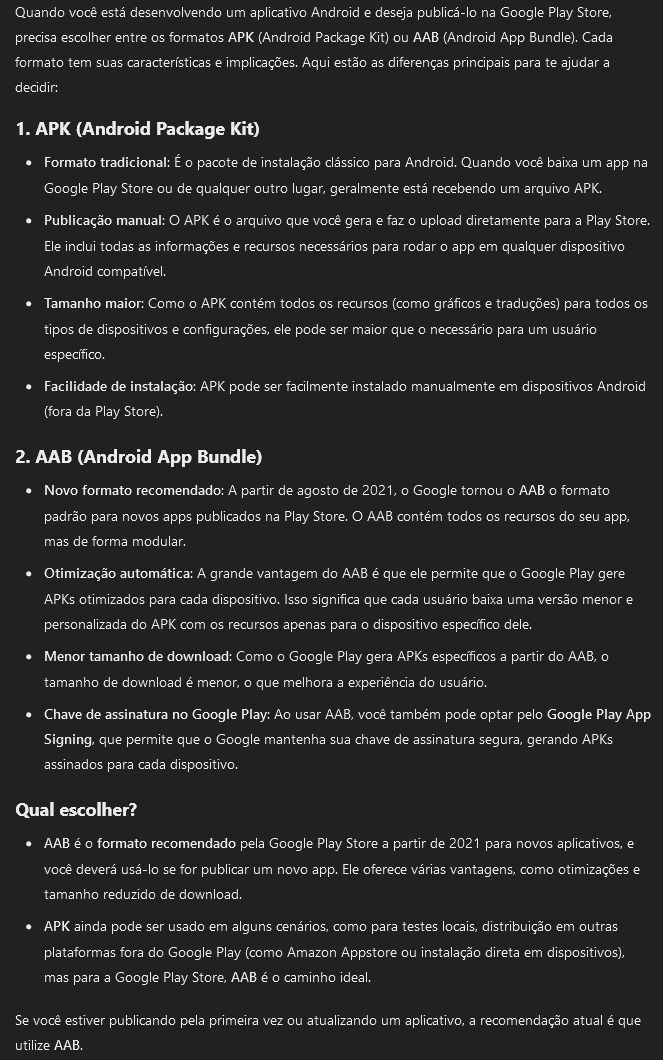 .
.
Google Play Services
-
Terrible tutorial about the subject .
-
It explains at the end of the video how to save the game using Google Play Services.
-
Uses Gradle, but does not say anything useful about it.
-
Firebase
-
API, authentication, analytics.
-
It is free as long as you have fewer than 10,000 users per month.