Types
Type conversion
-
You need to specify the type with
:. -
String to Int :
let a: u32 = "42".parse().expect("Falha!"); -
&str to String :
let a = "texto"; // &str let b = a.to_string(); // Stringlet a = String::from("texto");
Kinds of types
-
Compound Types:
-
Tuples and Arrays.
-
-
Scalar Types:
-
Everything else.
-
Boolean
fn main() {
let t = true;
let f: bool = false;
}
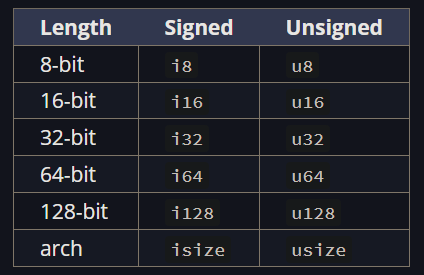
Integers
-
 .
.
-
" arch " varies depending on the system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
-
The primary situation in which you’d use
isizeorusizeis when indexing some sort of collection.
-
-
Signed and unsigned refer to whether it’s possible for the number to be negative.
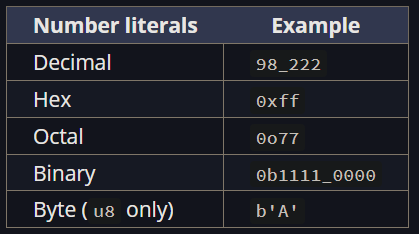
Number Literals
-
 .
.
-
Number literals can also use
_as a visual separator to make the number easier to read.
1_000
1000
Floats
-
All floating-point types are signed.
-
The default type is
f64because on modern CPUs, it’s roughly the same speed asf32but is capable of more precision.
fn main() {
let x = 2.0; // f64
let y: f32 = 3.0; // f32
}
Char
fn main() {
let c = 'z';
let z: char = 'ℤ'; // with explicit type annotation
let heart_eyed_cat = '😻';
}
-
"Your human intuition for what a “character” is may not match up with what a
charis in Rust."