-
-
Very good.
-
Watched everything, but skipped the eigenvector and eigenvalues part, as it wasn't relevant for what I'm doing.
-
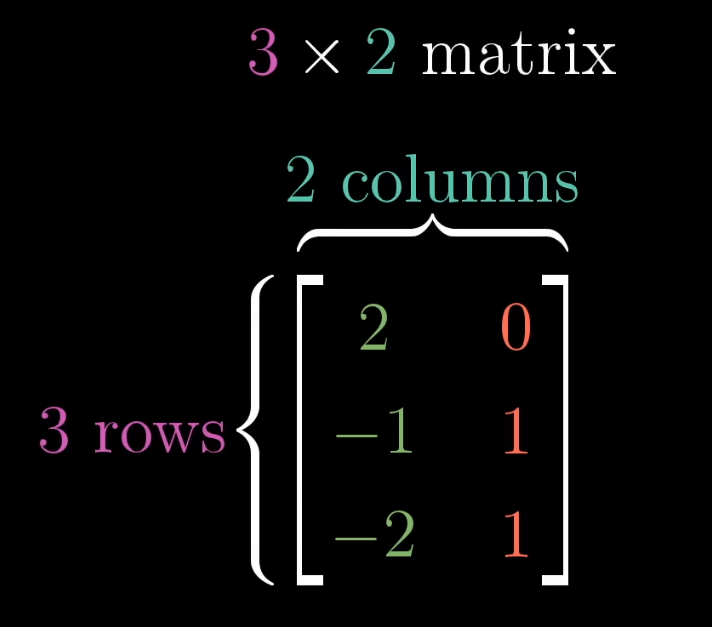
Matrix
-
 .
.
-
Maps 2 dimensions to 3 dimensions.
-
-
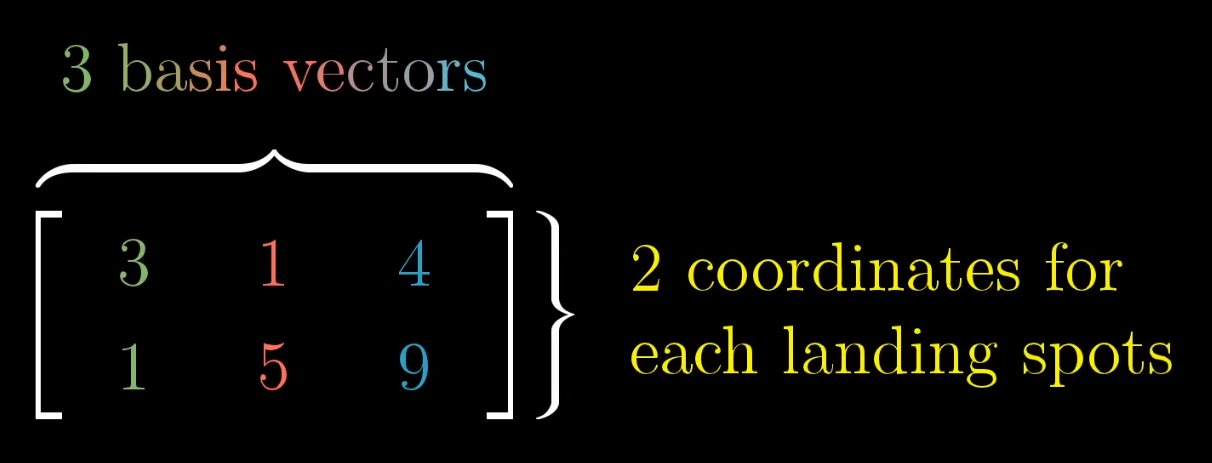 .
.
-
Maps 3 dimensions to 2 dimensions.
-
-
Matrix multiplication :
-
Matrices give us a language to describe transformations, where the columns represent those coordinates.
-
Matrix multiplication is just a way to compute what this transformation does to a given vector.
-
Any matrix can be interpreted as a transformation of space.
-
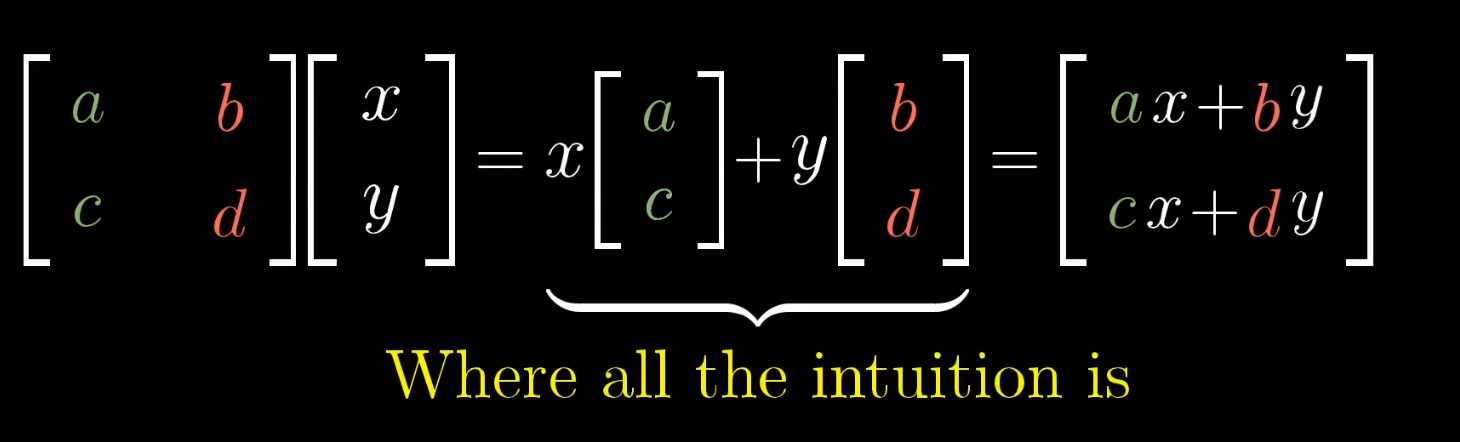 .
.
-
-
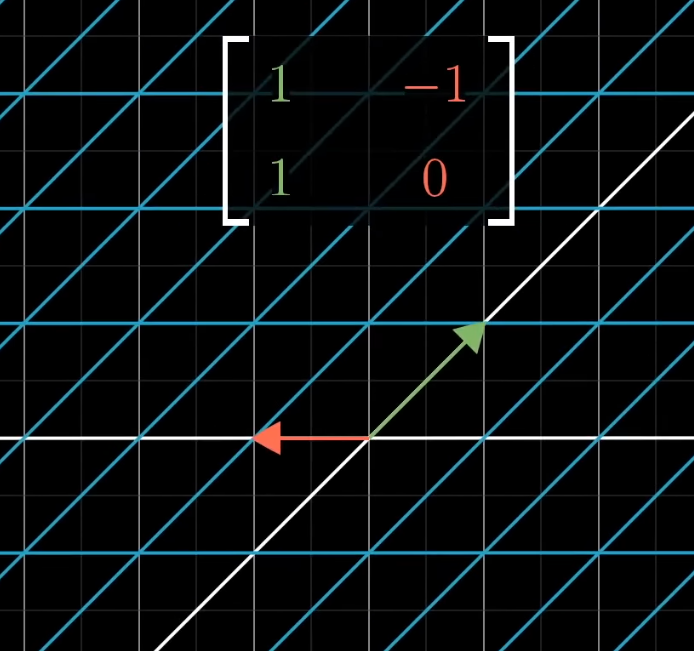
Matrix composition :
-
 .
.
-
i (green)will point to1, 1. -
j (red)will point to-1, 0. -
This constitutes a Rotation + Shear.
-
-
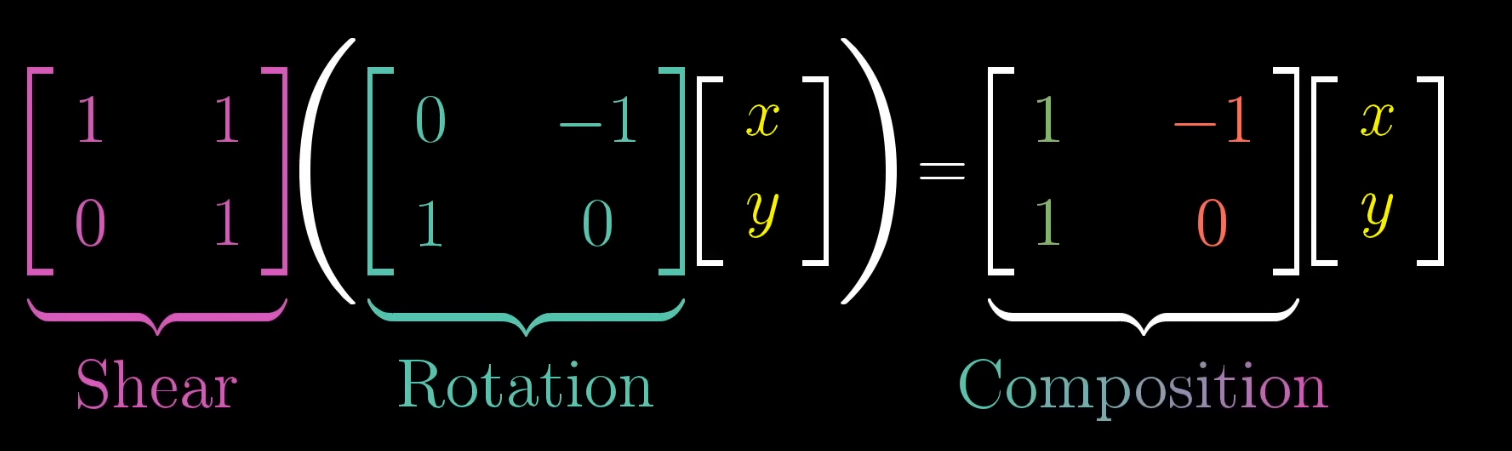 .
.
-
First apply the rotation, and then apply the shear.
-
This is the same as the composition 'rotation + shear'.
-
-
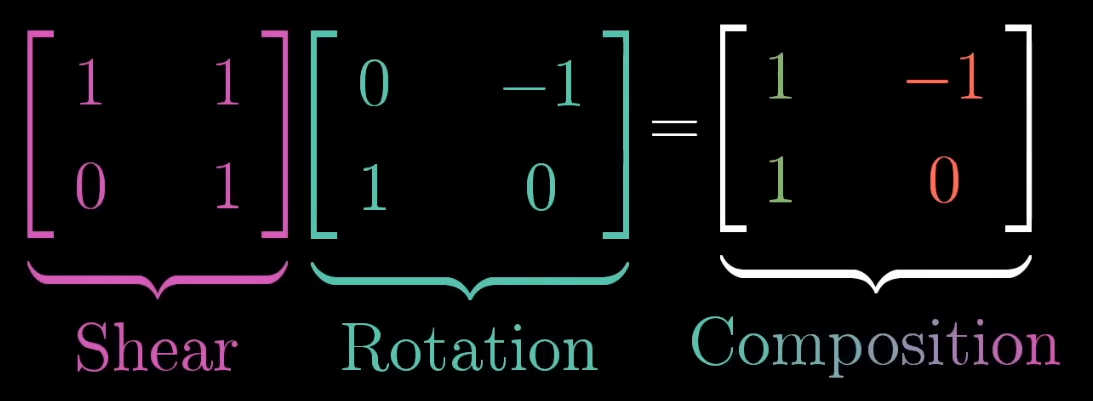 .
.
-
A composition has the same meaning as applying one transformation, then another.
-
This is read from right to left: the first transformation is Rotation, then Shear.
-
This comes from function notation
f(g(x)).
-
-
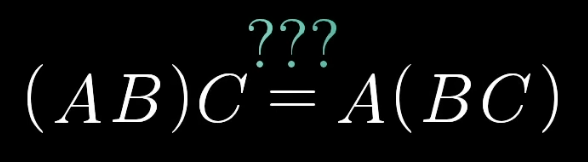 .
.
-
This is true, as you are just applying C, then B, then A, either way.
-
-
-
Determinant :
-
How much the AREA has scaled.
-
Or VOLUME if in 3D; imagine a 1x1x1 cube.
-
-
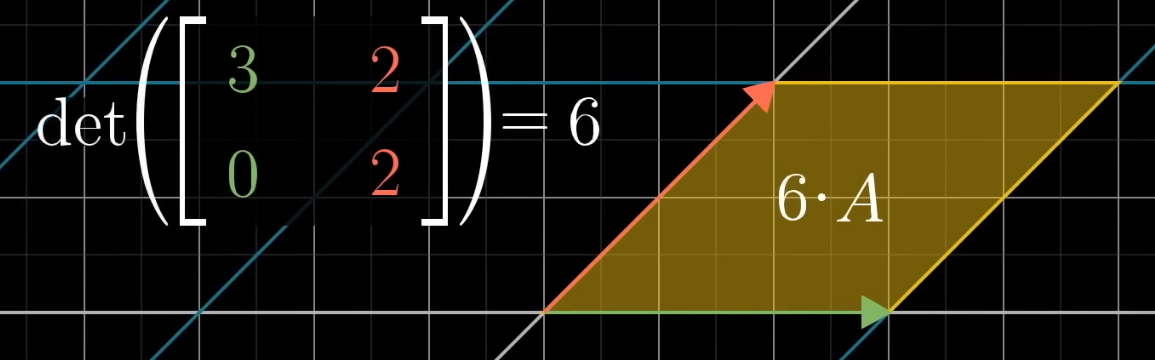 .
.
-
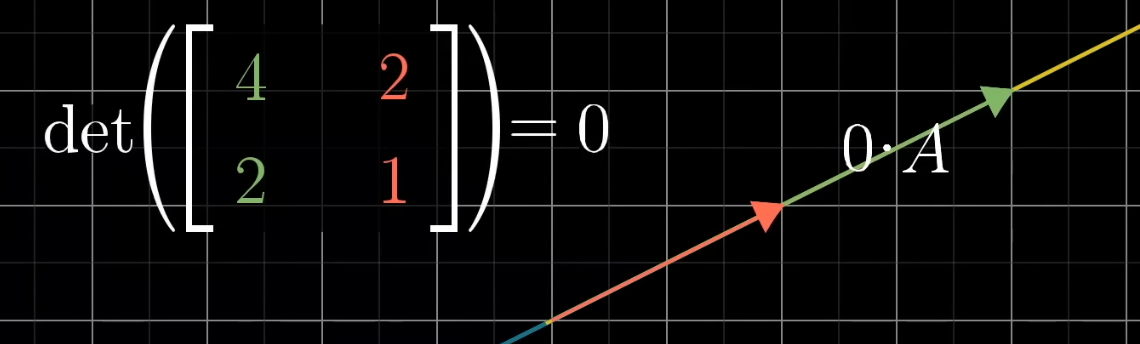 .
.
-
If the determinant is zero, it means that it squashes everything into a lower dimension.
-
-
If the determinant is negative, it means that the orientation is flipped (the space turns on itself) (a sheet of paper flips).
-
Calculation :
-
2D:
-
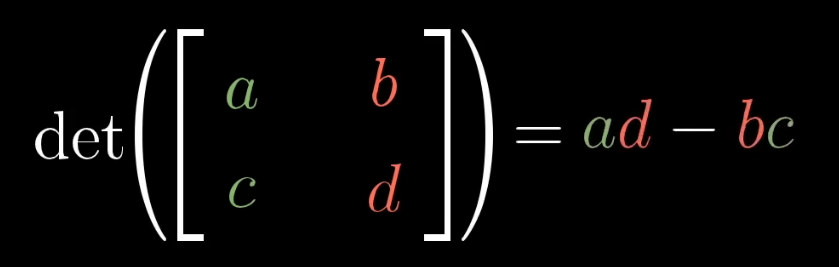 .
.
-
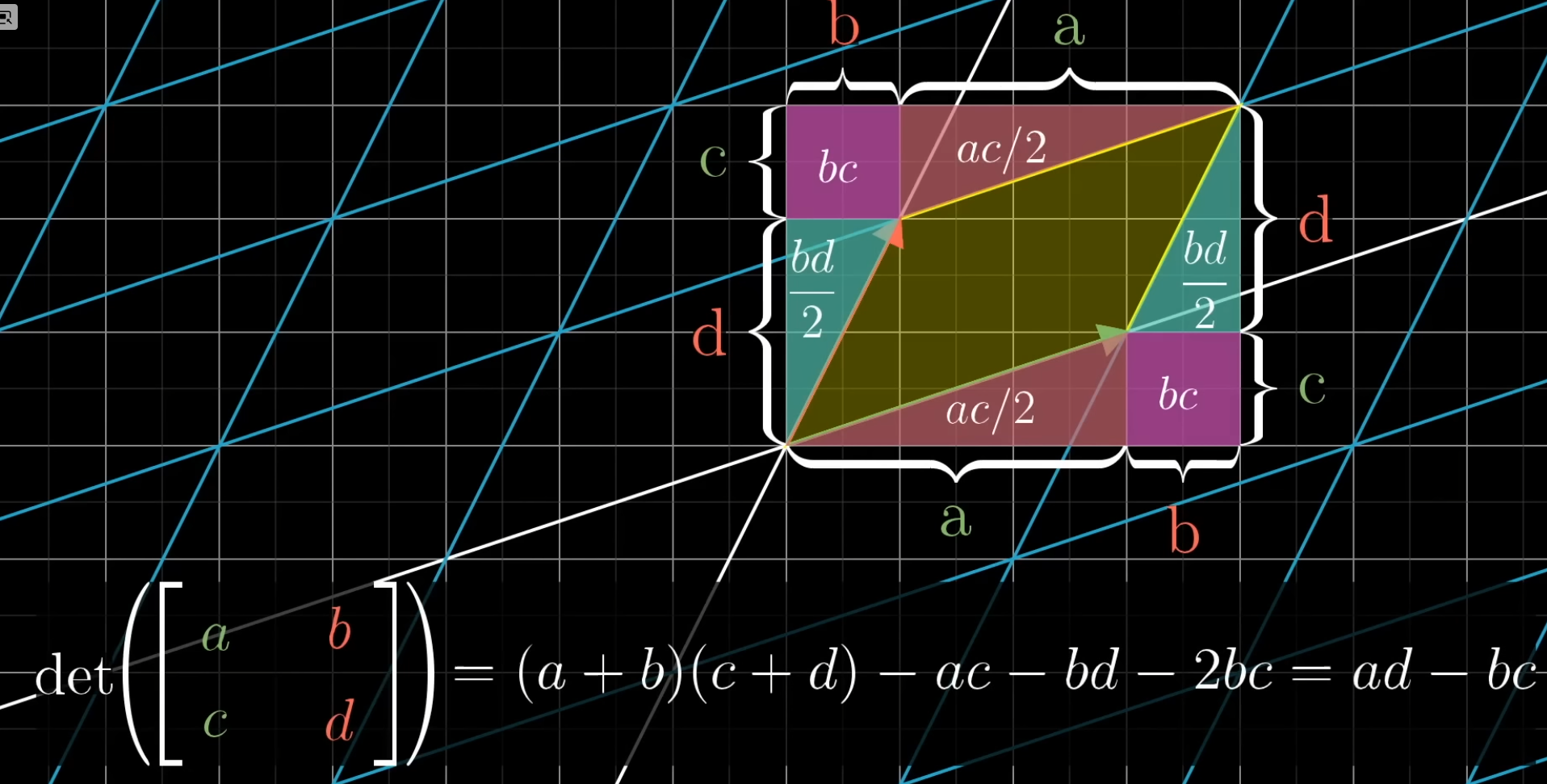
Proof:
 .
.
-
-
3D:
-
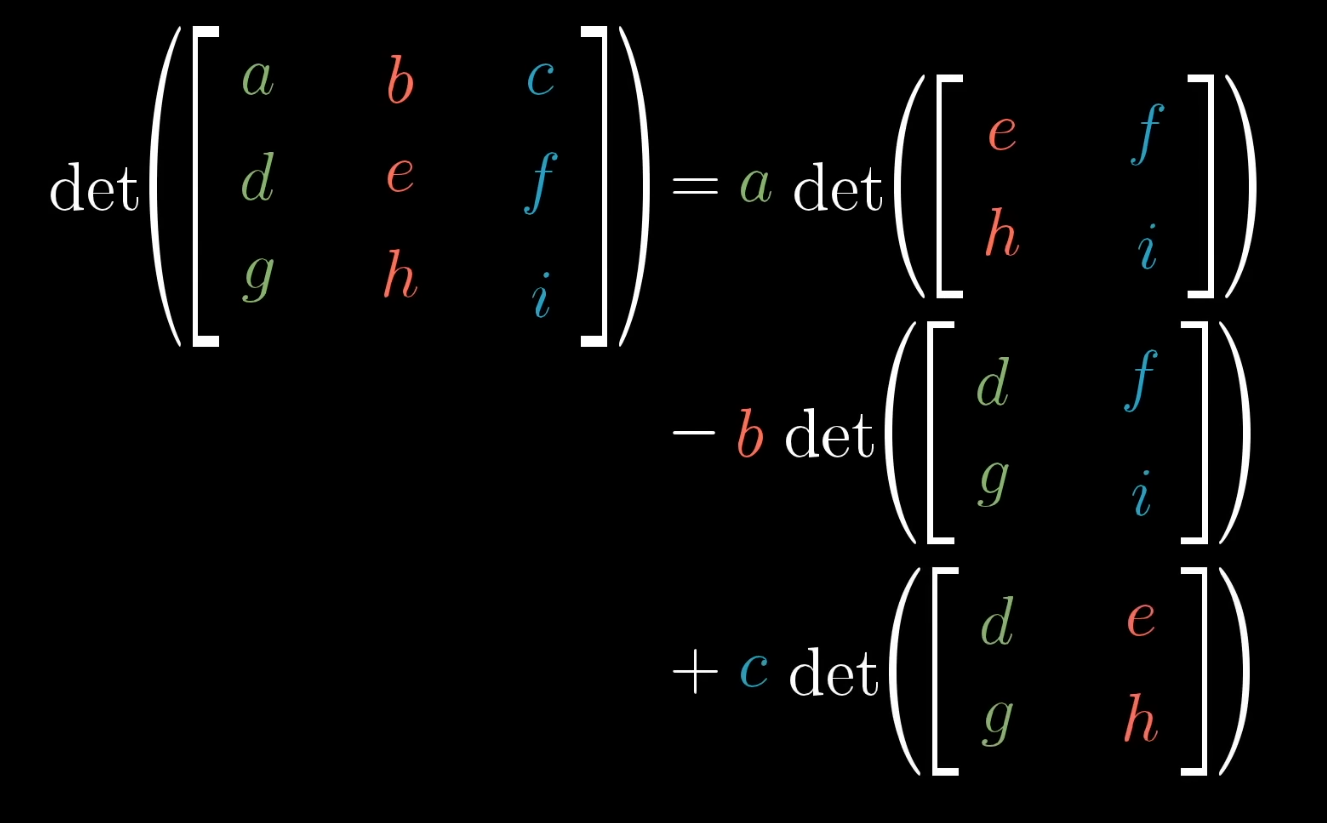 .
.
-
Proof: 'It's complicated and doesn't really make sense as the "essence of linear algebra"'.
-
-
-
-
System of equations :
-
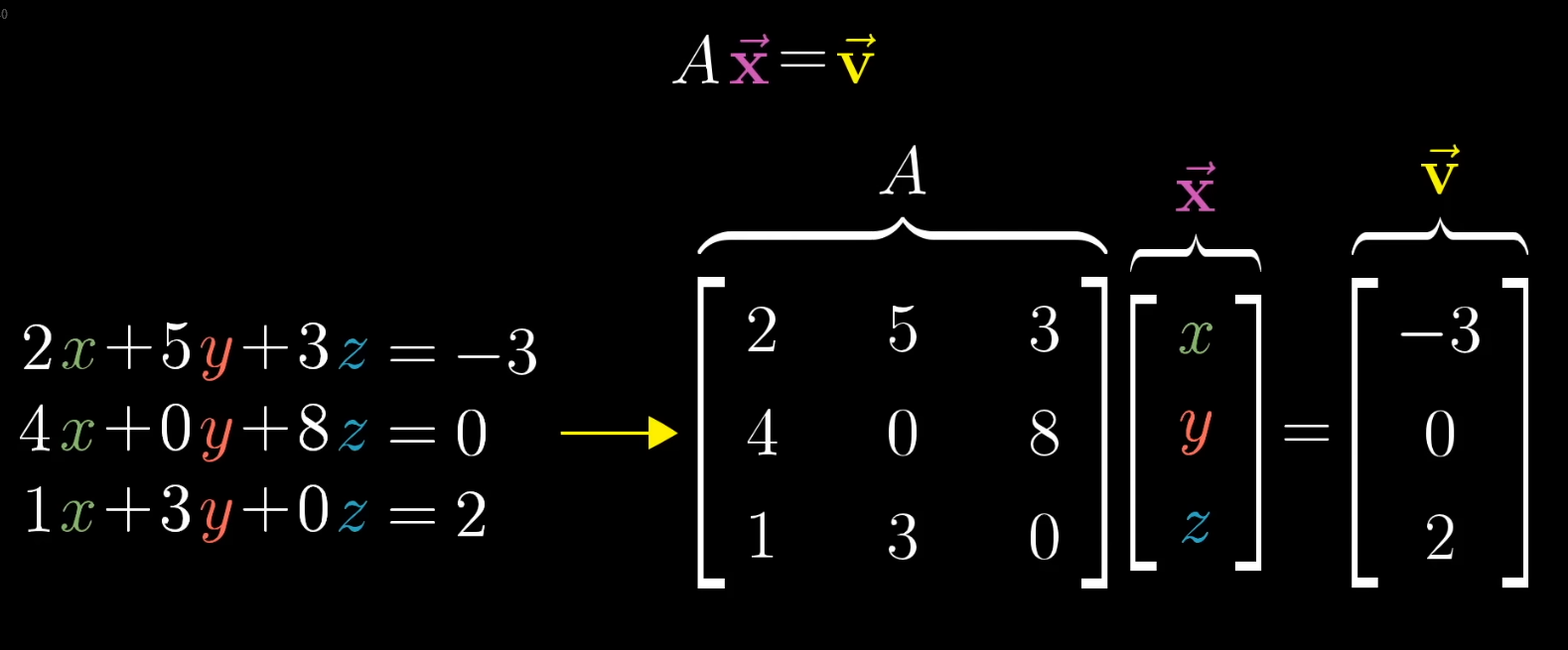 .
.
-
"Rank": number of dimensions in the output of a transformation.
-
"Column Space": Set of all possible outputs
Av
-
-
Inverse Matrix :
-
Does the inverse of a transformation.
-
If a matrix rotates 90º clockwise, the inverse of this would be rotating 90º counter-clockwise.
-
-
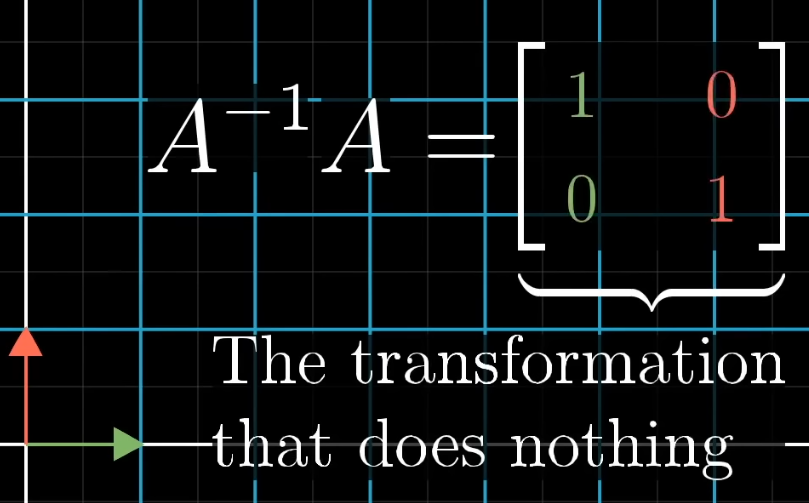 .
.
-
Doing the transformation A, and then doing the inverse of A, it's the same as not doing anything; hence the Identity Matrix.
-
-
OpenGL Normal Mapping Quote:
-
Note that we use the transpose function instead of the inverse function here. A great property of orthogonal matrices (each axis is a perpendicular unit vector) is that the transpose of an orthogonal matrix equals its inverse. This is a great property as inverse is expensive and a transpose isn't.
-
-
-
Dot Product :
-
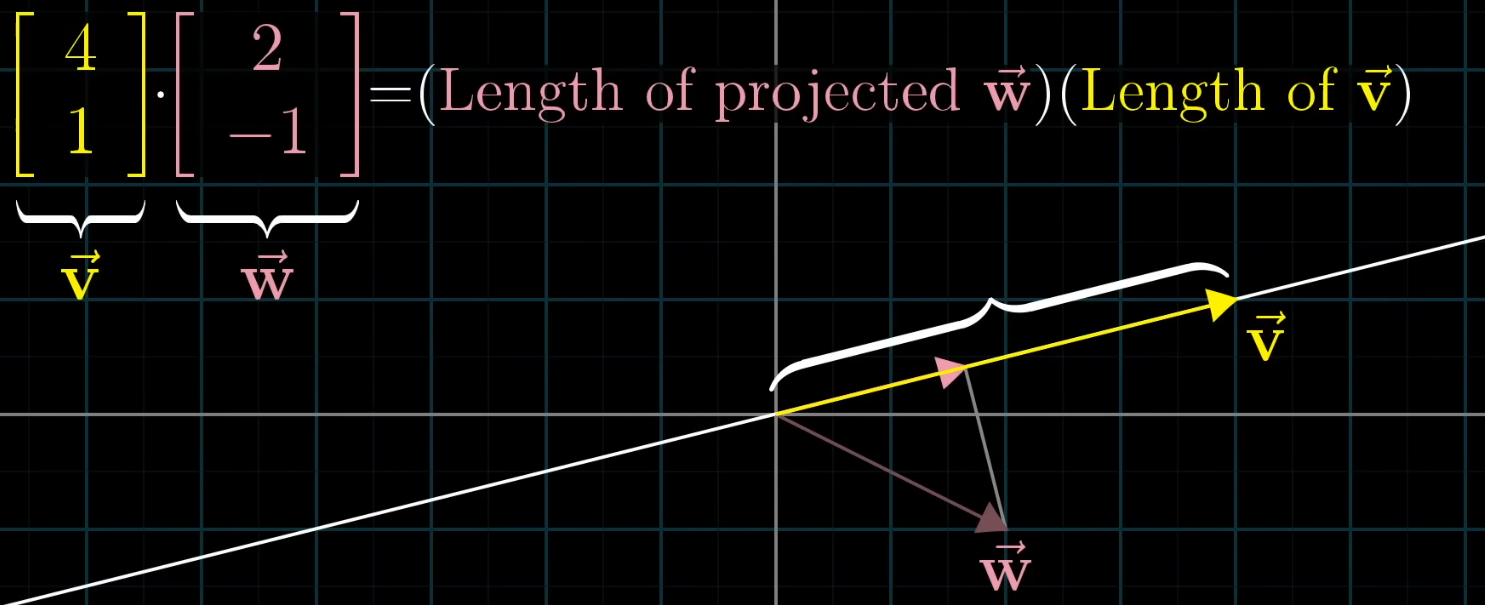 .
.
-
Usually used to analyze the angle between two vectors:
-
a.b > 0: angle less than 90º. -
a.b = 0: angle equal to 90º. -
a.b < 0: angle greater than 90º. -
If the value is positive, it means the vectors point "in the same direction".
-
-
-
Cross Product :
-
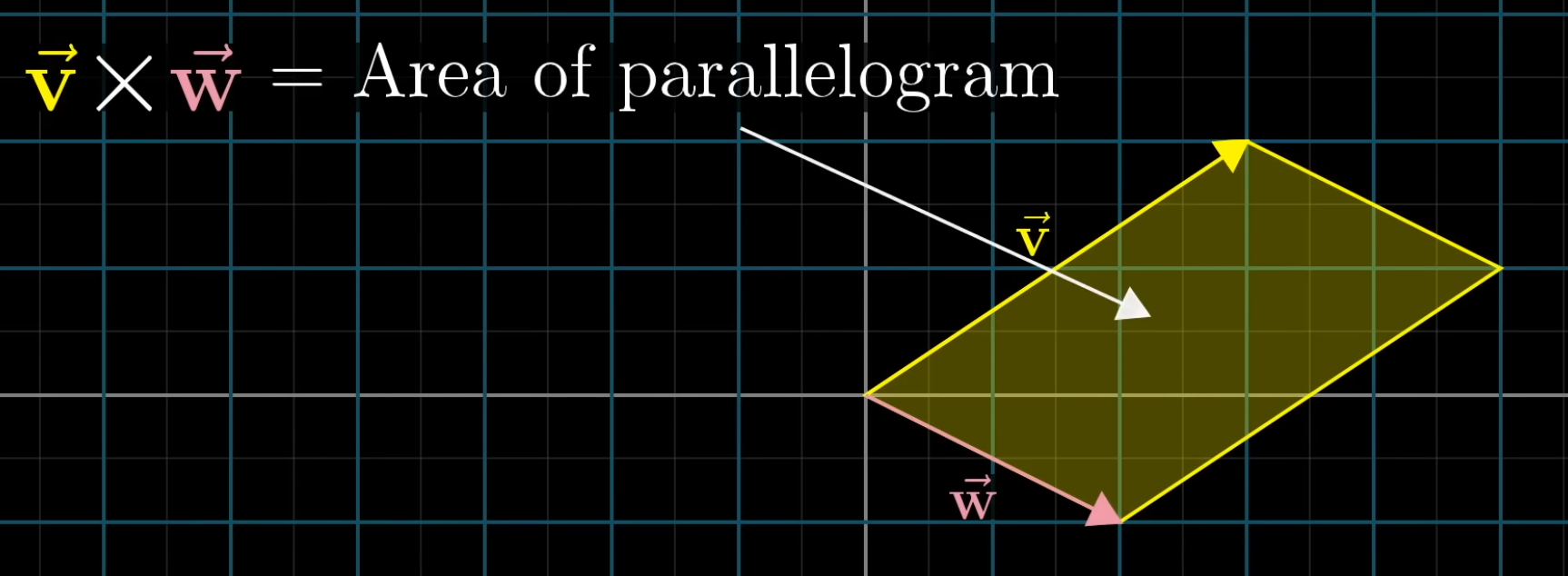 .
.
-
Calculating:
-
The Cross Product is just the determinant of the matrix, as the determinant computes the AREA of the matrix.
-
Also, consider the orientation.
-
-
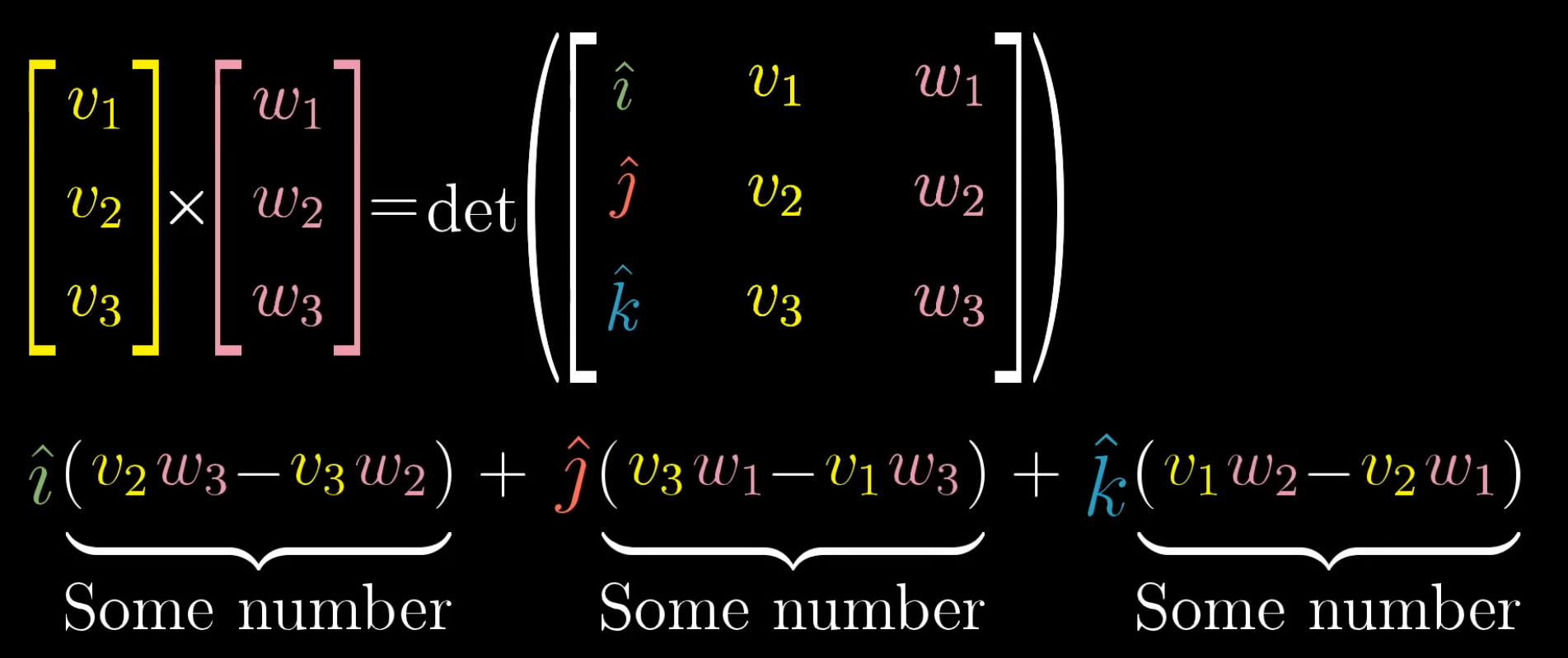 .
.
-
This is a mathematical trick to "help" calculate the determinant above.
-
-
-
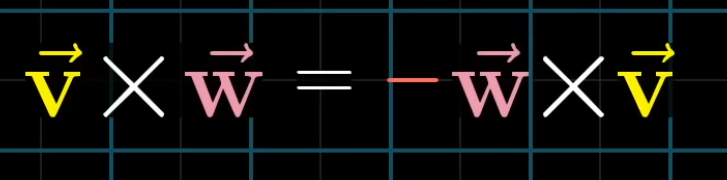
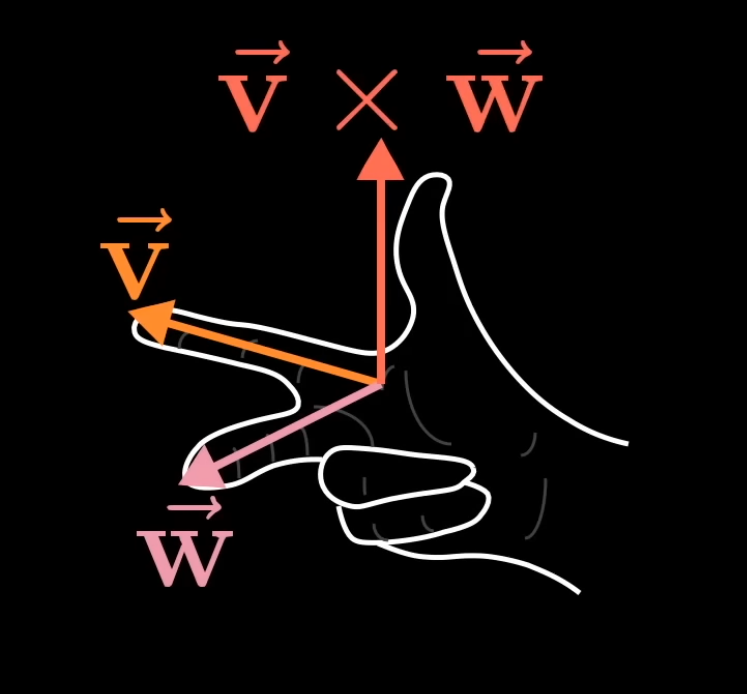
Orientation:
-
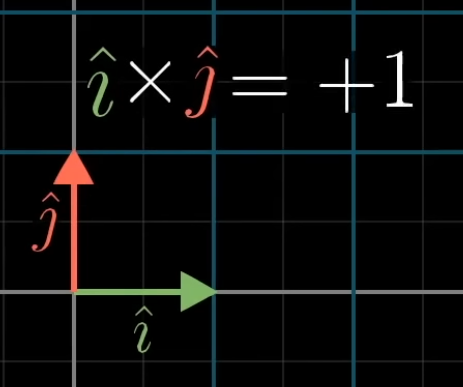 .
.
-
 .
.
-
 .
.
-
-
-
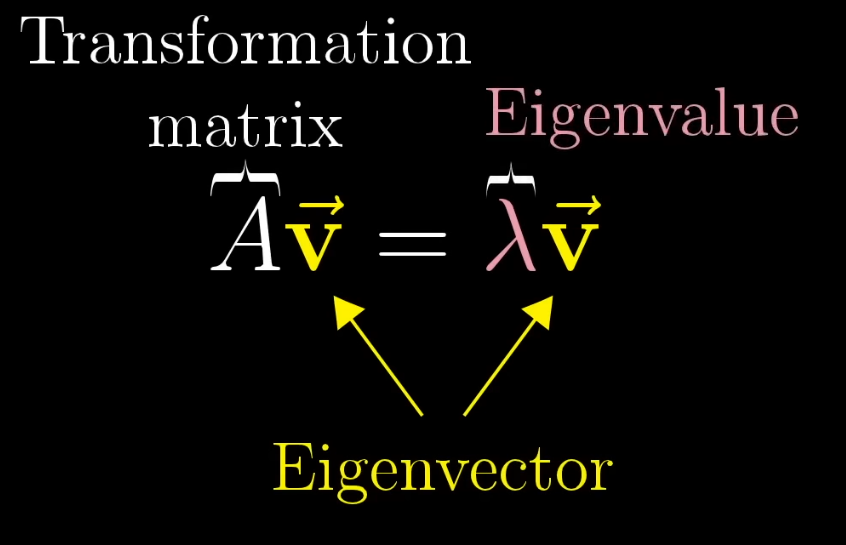
Eigenvector and Eigenvalues :
-
Eigenvector: A vector that remains in its own span.
-
 .
.
-
Quaternions
-
Zero rotation :
-
(0, 0, 0, 1).
-
-
Quaternion multiplication :
-
Is rotation composition.
-
In the context of 3D rotations, multiplication is the only operation that directly corresponds to combining or applying rotations.
-
Non-commutativity matters:
q2q1≠q1q2. This matches the non-commutativity of rotation matrices.
-
-
Quaternion conjugate / inverse :
-
The conjugate of a unit quaternion is its inverse.
-
Needed when rotating vectors: $qvq^{−1}$.
-
Useful for undoing a rotation.
-
-
Quaternion scalar multiplication :
-
Not used for representing rotations, since only unit quaternions encode valid rotations.
-
-
Quaternion addition :
-
Is averaging rotation.
-
ChatGPT:
-
Addition of quaternions has no direct geometric meaning for rotations.
-
It can be used in interpolation schemes (e.g., normalized linear interpolation), but addition itself is not a “rotation operation”.
-
-
-
Why Use Quaternions in Graphics :
-
Numerical stability : avoids gimbal lock (unlike Euler angles).
-
Compactness : 4 numbers vs 9 in a matrix.
-
Efficient interpolation : spherical linear interpolation (slerp) is defined directly on quaternions, which is critical for animation blending.
-
Fast composition : quaternion multiplication is cheaper than matrix multiplication.
-
-
Euler to Quaternion :
-
quaternion_from_euler_angles().-
The order is specified via
Euler_Angle_Order. -
See more at Odin#Quaternion .
-
-
Let:
-
roll = α (rotation around X)
-
pitch = β (rotation around Y)
-
yaw = γ (rotation around Z)
-
-
Assume intrinsic rotation order Z → Y → X (common convention in graphics).
-
Quaternion (w, x, y, z):
w = cos(α/2) * cos(β/2) * cos(γ/2) + sin(α/2) * sin(β/2) * sin(γ/2) x = sin(α/2) * cos(β/2) * cos(γ/2) - cos(α/2) * sin(β/2) * sin(γ/2) y = cos(α/2) * sin(β/2) * cos(γ/2) + sin(α/2) * cos(β/2) * sin(γ/2) z = cos(α/2) * cos(β/2) * sin(γ/2) - sin(α/2) * sin(β/2) * cos(γ/2) -
The above assumes Z-Y-X order (yaw → pitch → roll). If your engine uses a different Euler order, the formulas change.
-
Always normalize the quaternion after conversion from Euler to keep it valid.
-
-
Quaternion to Euler :
-
euler_angles_from_quaternion().-
The order is specified via
Euler_Angle_Order. -
See more at Odin#Quaternion .
-
-
Given quaternion
(w, x, y, z):
pitch (β) = asin( 2 * (w*y - z*x) ) yaw (γ) = atan2( 2 * (w*x + y*z), 1 - 2*(x*x + y*y) ) roll (α) = atan2( 2 * (w*z + x*y), 1 - 2*(y*y + z*z) )-
The above assumes Z-Y-X order (yaw → pitch → roll). If your engine uses a different Euler order, the formulas change.
-
atan2is the 2-argument arctangent, which handles quadrant correctly. -
Gimbal lock happens if pitch = ±90°. In that case, roll and yaw are not uniquely defined.
-
-
~ Understanding Quaternions for Game Dev .
-
Critiques the explanations by 3blue1brown and numberfy for complicating the concept by introducing 4D spheres.
-
His explanation is based on defining a rotation axis, etc.
-
His intent to simplify the process is fine, but there is no foundational reasoning; it feels like rote memorization.
-
For graphics programming, this is probably the only explanation that makes sense to look at; 3blue1brown's is somewhat irrelevant, curiously.
-
-
~ Quaternion and 3D Rotation .
-
Yeah, nothing useful for computer graphics could be understood.
-
-
~ Visualization of Quaternions as a 4D sphere .
-
Only provides several images to help visualize the 4D sphere, nothing more.
-
Yeah, nothing useful for computer graphics could be understood.
-
-
 .
.
Etc
Spherical Coordinates
-
From spherical to Cartesian
-
 .
.
-
-
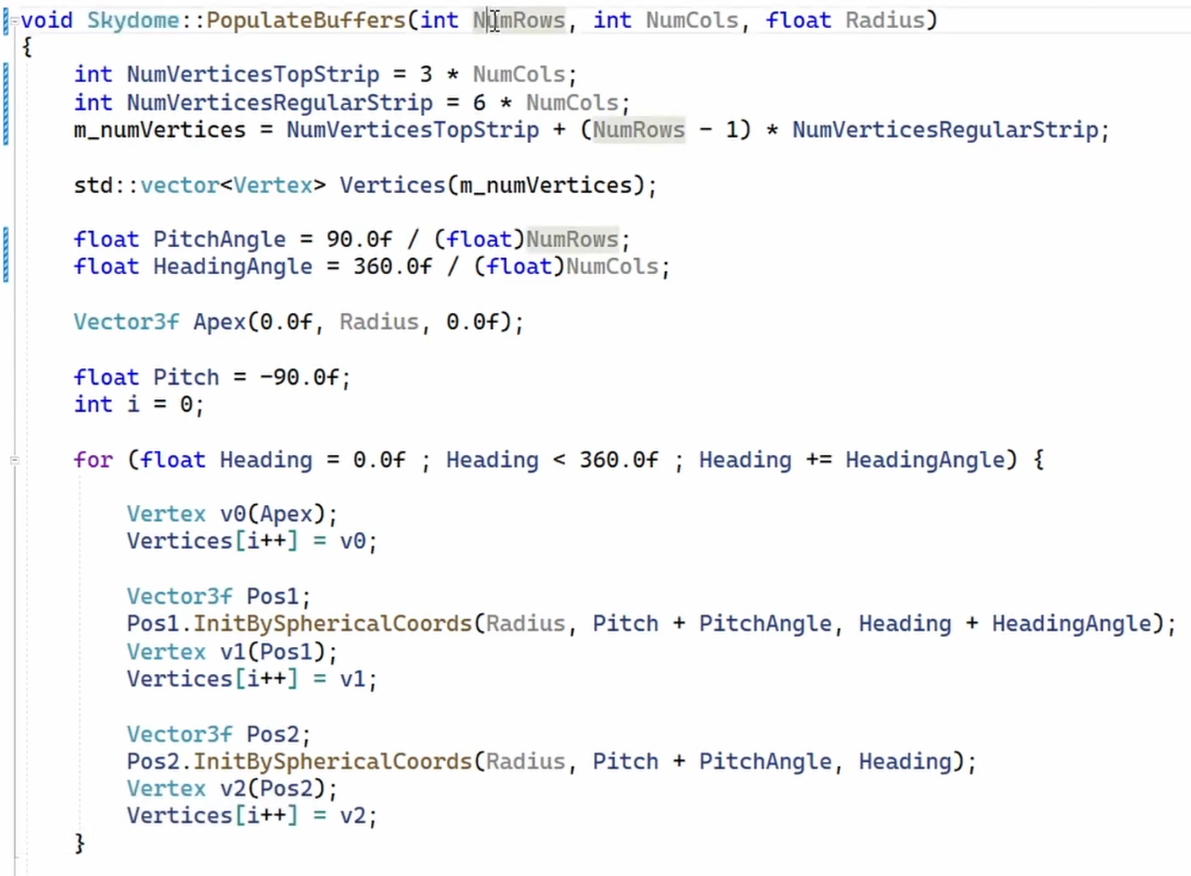
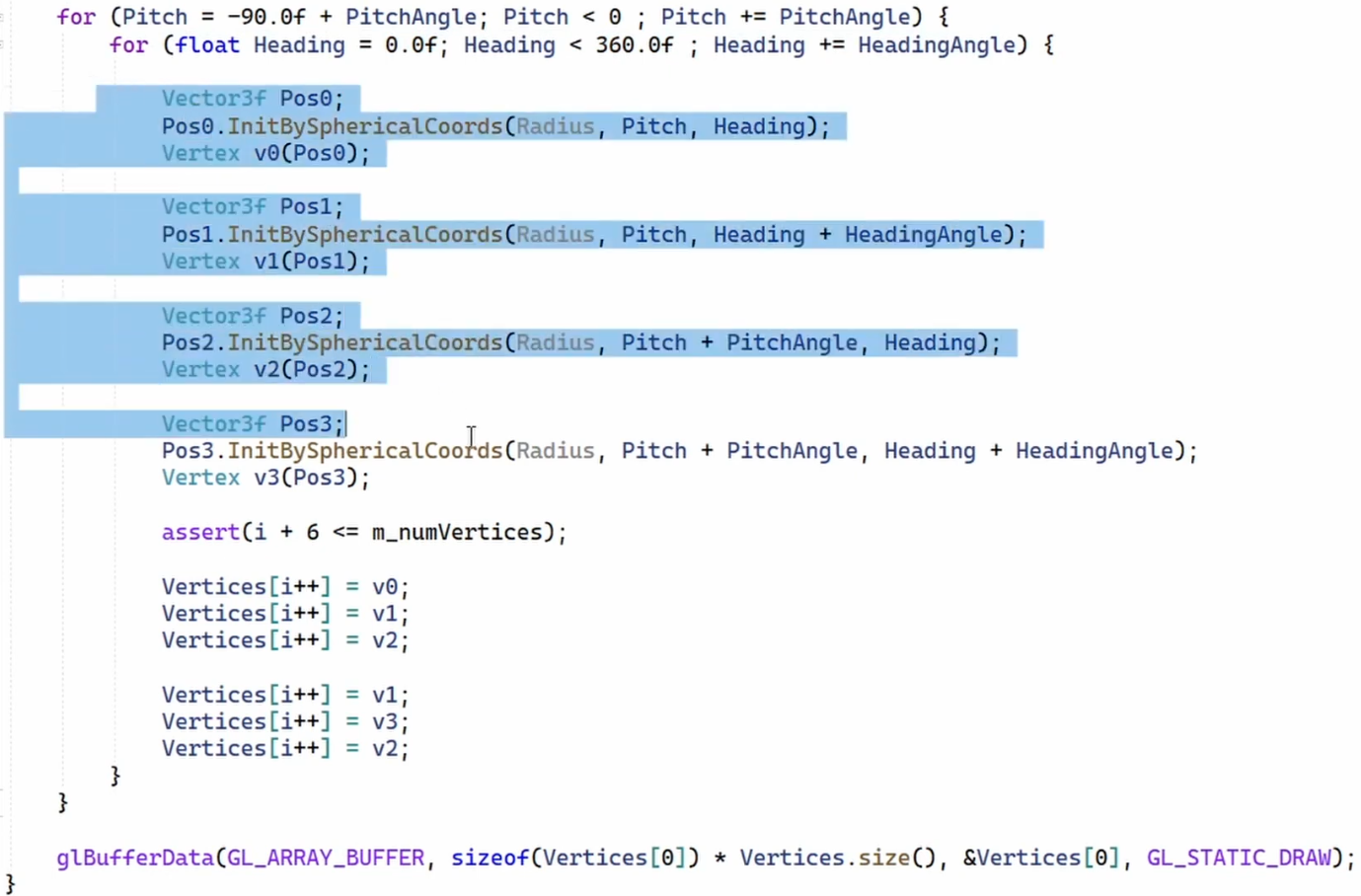
Skydome :
 .
.
 .
.